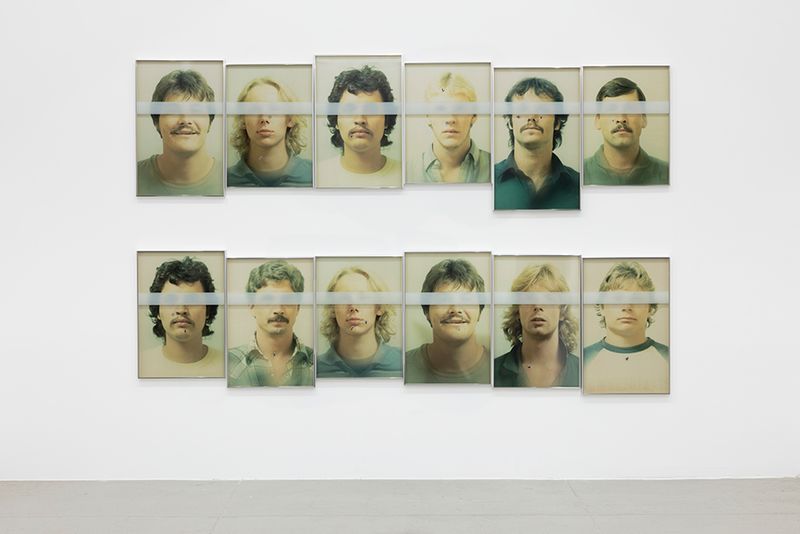

Serialities
15 February - 8 April 2017
New York, 22nd Street
Installation views
About the Artists

Roni Horn
La obra de Roni Horn se caracteriza por la incertidumbre y la imposibilidad de concluirla. En toda su obra es importante su interés por la naturaleza mutable de la identidad, el significado y la percepción, así como la noción de duplicidad, cuestiones que siguen impulsando la práctica de Horn.

PAUL McCARTHY
Paul McCarthy is widely considered to be one of the most influential and groundbreaking contemporary American artists. Born in 1945, and raised in Salt Lake City, Utah, he first established a multi-faceted artistic practice, which sought to break the limitations of painting by using unorthodox materials such as bodily fluids and food. He has since become known for visceral, often hauntingly humorous work in a variety of mediums—from performance, photography, film and video, to sculpture, drawing and painting.
During the 1990s, he extended his practice into installations and stand-alone sculptural figures, utilizing a range of materials such as fiberglass, silicone, animatronics and inflatable vinyl. Playing on popular illusions and cultural myths, fantasy and reality collide in a delirious yet poignant exploration of the subconscious, in works that simultaneously challenge the viewer’s phenomenological expectations.
Whether absent or present, the human figure has been a constant in his work, either through the artist‘s own performances or the array of characters he creates to mix high and low culture, and provoke an analysis of our fundamental beliefs. These playfully oversized characters and objects critique the worlds from which they are drawn: Hollywood, politics, philosophy, science, art, literature, and television. McCarthy’s work, thus, locates the traumas lurking behind the stage set of the American Dream and identifies their counterparts in the art historical canon.
McCarthy earned a BFA in painting from the San Francisco Art Institute in 1969, and an MFA in multimedia, film and art from USC in 1973. For 18 years, he taught performance, video, installation, and art history in the New Genres Department at UCLA, where he influenced future generations of west coast artists and he has exhibited extensively worldwide. McCarthy’s work comprises collaborations with artist-friends such as Mike Kelley and Jason Rhoades, as well as his son Damon McCarthy.
Eva Hesse
Born in Hamburg Germany in 1936, Eva Hesse is one of the icons of American art of the 1960s, her work being a major influence on subsequent generations of artists. Comprehensive solo exhibitions in the past 50 years, as well as a retrospective that toured from the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art to the Museum Wiesbaden in Germany and finally to the Tate Modern in London, have highlighted the lasting interest that her oeuvre has generated. Hesse cultivated mistakes and surprises, precariousness and enigma, to make works that could transcend literal associations. The objects she produced, at times barely present yet powerfully charismatic, came to play a central role in the transformation of contemporary art practice.
In New York in the 1960s, Hesse was one of a group of artists, including Robert Morris, Bruce Nauman, Richard Serra and Robert Smithson, who engaged with materials that were flexible, viscous or soft: latex rubber, plastic, lead, polythene, copper, felt, chicken-wire, dirt, sawdust, paper pulp and glue. Often unstable and subject to alteration, these elements yielded works that were vital in their relativity and mutability. Hesse was aware she produced objects that were ephemeral, but this problem was of less concern to her than the desire to exploit materials with a temporal dimension. Much of the life-affirming power of Hesse’s art derives from this confident embrace of moment. As she stated in an interview with Cindy Nemser for Artforum in 1970, 'Life doesn’t last; art doesn’t last.'

Zoe Leonard
New York-based artist Zoe Leonard balances rigorous conceptualism with a distinctly personal vision in her work, which merges photography, sculpture, and installation. By employing strategies of repetition, shifting perspectives, and a multitude of printing processes, Leonard’s practice probes the politics of representation and display. Leonard explores themes such as gender and sexuality, loss and mourning, migration, displacement, and the urban landscape. Her photography specifically invites us to contemplate the role that the medium plays in constructing history, and to consider the roots of contemporary photographic culture. More than its focus on any particular subject, however, Leonard’s work encourages the viewer to reconsider the act of looking itself, drawing attention to observation as a complex, ongoing process.

David Smith
David Smith is regarded as one of the most innovative artists and important American sculptors of the 20th century. He transformed sculpture by rejecting the traditional methods of carving and casting in favor of torch-cutting and welding, becoming the first artist known to make welded sculpture in America. These methods allowed him to work in an improvisational manner in creating open and large-scale, abstract sculptures. In his later years, he installed his sculptures in the fields of his home in the Adirondack Mountains, where a dialogue between the art object and nature emerged as central to his practice. His sculpture-filled landscape inspired Storm King Art Center and other sculpture parks throughout the world, as well as anticipating the land and environmental art movements.
Smith was born in 1906 in Decatur, Indiana. He worked briefly as a welder in an automobile factory before moving to New York City to become an artist in 1926. He studied painting at the Art Students league, where Cubism and Surrealism were foundational to his practice. He began welding sculpture around 1933 after seeing reproductions of constructed steel sculptures by Pablo Picasso and Julio González. He later became associated with the abstract expressionist movement and paved the way for minimalism with radically simplified, geometric works. Painting and drawing remained integral to what Smith called his ’work stream’. He embraced a holistic attitude toward artmaking and dismissed the idea of a separation between mediums. Acknowledging the tradition of painted sculpture throughout art history and drawing from the bold palettes of modernism and pop culture, Smith often painted his sculptures. David Smith died in 1965, leaving behind an expansive, complex, and powerful body of work that continues to exert influence upon subsequent generations of artists.
Smith began exhibiting his work as early as 1930. His first survey was organized by the Museum of Modern Art, New York in 1957. His sculpture was represented by the United States at the São Paulo Biennale in 1951 and at the Venice Biennale in 1954 and 1958. Posthumous retrospectives have been held at the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum (1979 and 2006, which traveled to Tate Modern, London and the Centre Pompidou, Paris) and at the Los Angeles County Museum of Art (2011, which traveled to the Whitney Museum of American Art, New York and the Wexner Center for the Arts, Columbus, Ohio). Other major surveys have been organized at the Sezon Museum of Art, Tokyo (1994, traveled throughout Japan), the Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, Madrid (1996), Storm King Art Center (1997–99), and Yorkshire Sculpture Park, Wakefield, UK. A three-volume, fully illustrated catalogue raisonné of Smith’s sculpture was published in 2021 by the Estate of David Smith and distributed by Yale University Press. A biography by Michael Brenson, David Smith: The Art and Life of a Transformational Sculptor, was published by Farrar, Straus, and Giroux in 2022.
Current Exhibitions
1 / 12





































